Research


Spectroscopic single-molecule localization microscopy or sSMLM (super-resolution optical imaging)
We developed a technology referred to as spectroscopic single-molecule localization microscopy or sSMLM. We showed that sSMLM can detect fluorescence emissions from single molecules with a spatial resolution of 5 nm and a spectral resolution of 0.6 nm, simultaneously. We are using sSMLM to investigate various biological processes and we are also pushing the limits of sSMLM through novel optical designs.
We developed an open-source Image-J plug-in called RainbowSTORM for sSMLM data processing. Please try and provide your feedback.
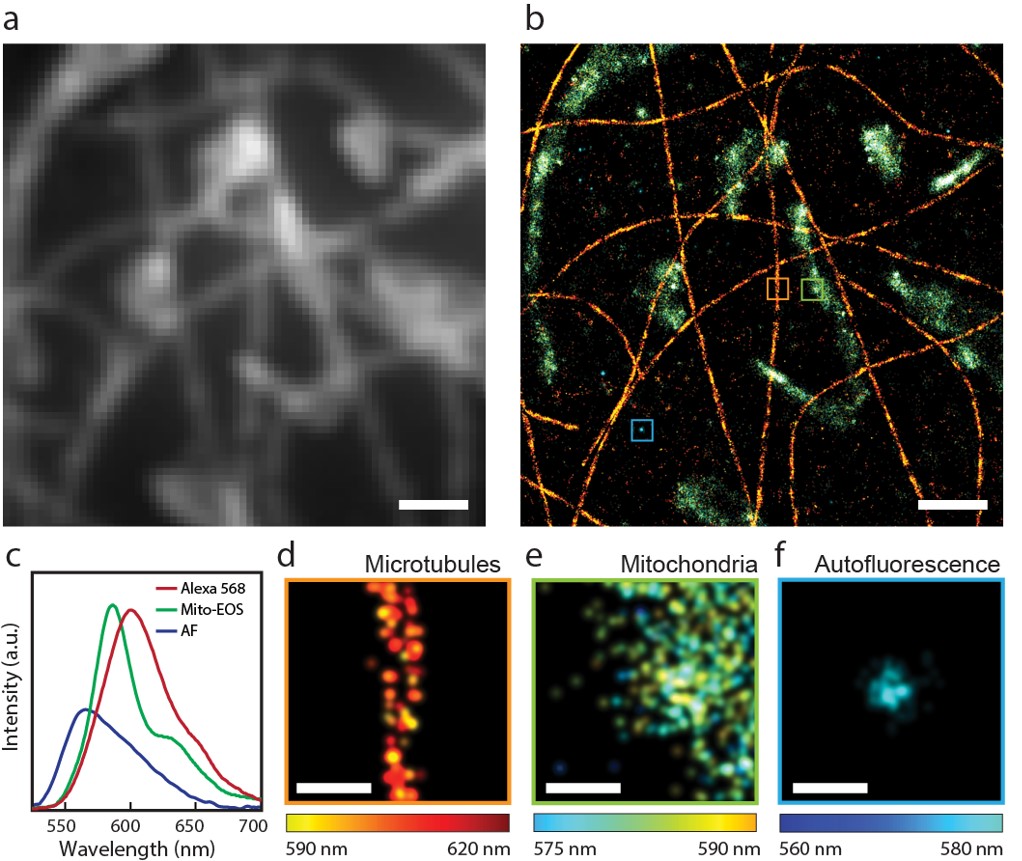
Capability of sSMLM to image multiple fluorescence contrasts simultaneously, even when their emission spectra are highly overlapping.
Isolated chromosomes imaged by sSMLM (left) and its associated reconstruction process (right).
An intact cell nucleus imaged by sSMLM (left) and its associated reconstruction process (right).
Collaborators:
Prof. Cheng Sun, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University
Prof. Vadim Backman, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Northwestern University
Prof. Daniela E Matei, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Northwestern University
Prof. Mazhar Adli, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Northwestern University
Visible-light optical coherence tomography
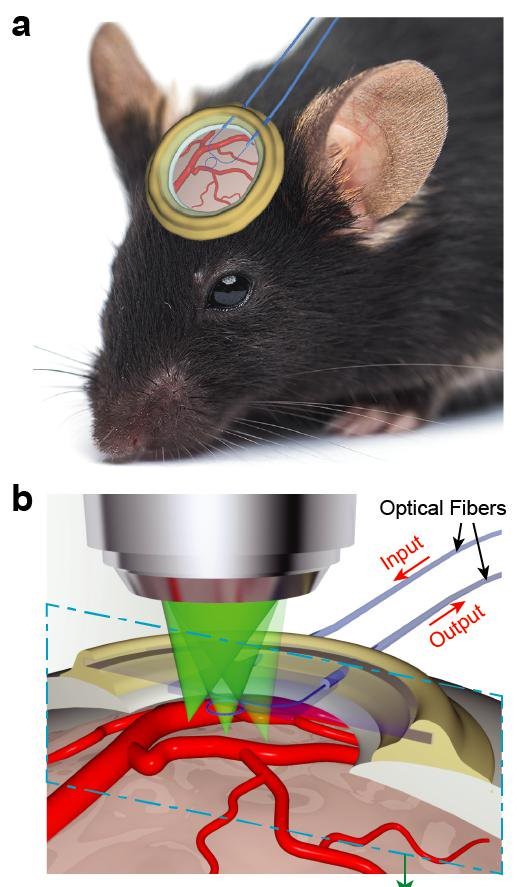
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an optical interference based high-speed, high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging technology with wide-spread applications in both fundamental biomedical investigations and clinical diagnoses / management of various diseases. We focus on developing OCT technologies for hemodynamic and new functional imaging and ultrahigh spatial resolution imaging. Using visible light, instead of near-infrared light, illumination in OCT and combining with our sophisticated inverse algorithms, we are able to image the complete metabolic parameters, including blood flow, hemoglobin oxygen saturation, and metabolic rate of oxygen, in microcirculations. We apply our functional OCT technology to better understand blinding diseases and visual functions.
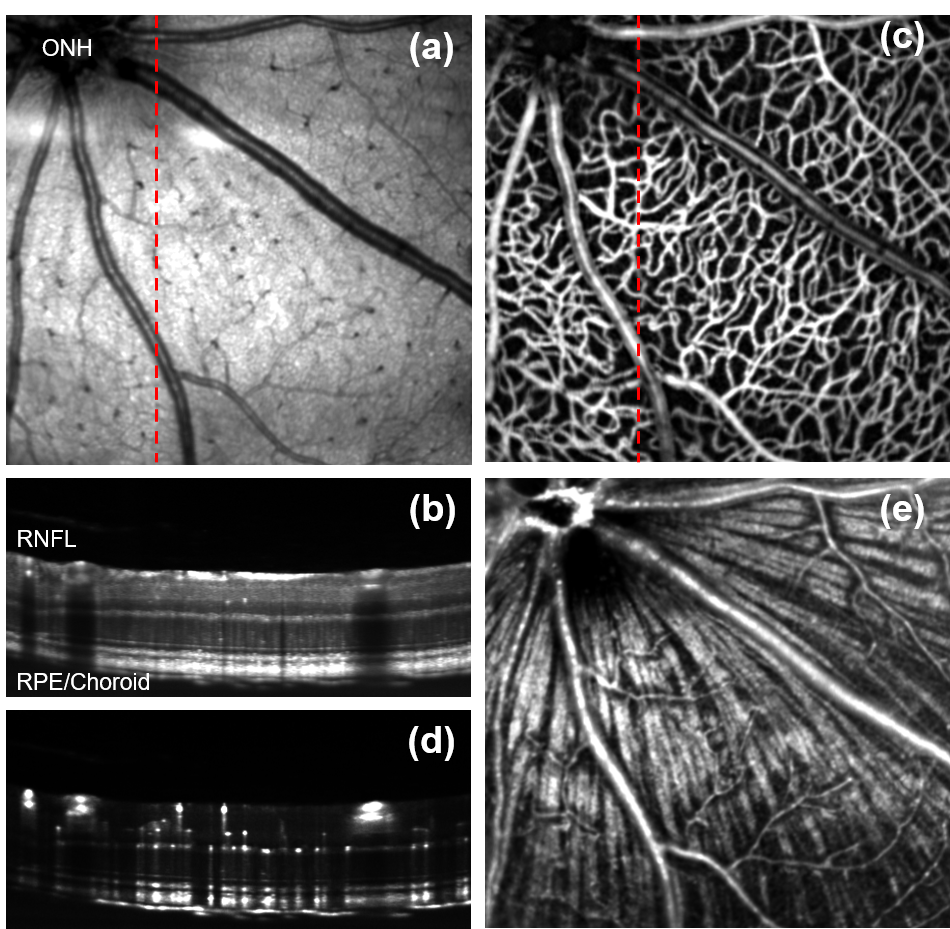
Visible-light OCT images of a mouse eye showing (a) En face fundus; (b) B-scan image; (c) En face angiogran; (d) B-scan angiogram; (e) Fibergram.
.gif)
Vis-OCT B-scan images fly-through
Nano/micro fabrication and photoacoustic imaging
Working with collaborators, we design and fabricat novel micro-photonic devices for imaging and sensing. One photonic device we use is the optical micro-ring resonator. When fabricated in compressible polymer materials, optical micro-ring resonators can be used as ultra-sensitive ultrasonic detectors for photoacoustic microscopy. Moreover, we fabricate these micro-photonic devices on optically-transparent substrate to enable easy integration of photoacoustic microscopy with other established optical microscopic technologies such as OCT and confocal microscopy.
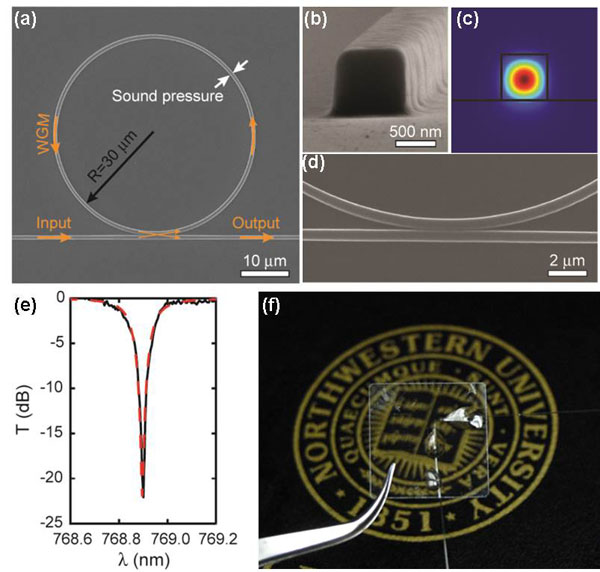
Collaborator
Prof. Cheng Sun, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Northwestern University
Ophthalmic imaging
We develop novel retinal imaging system to study early metabolic variation and retinal pigment epithelium dysfunctions to achieve early diagnosis and better understanding of ischemia-driven retinopathy and age-related retinal degeneration. We explore multimodal and functional imaging technologies for more comprehensive retinal imaging. Our technologies mainly focus on visible-light optical coherence tomography, and other types of fluorescence imaigng modalities.
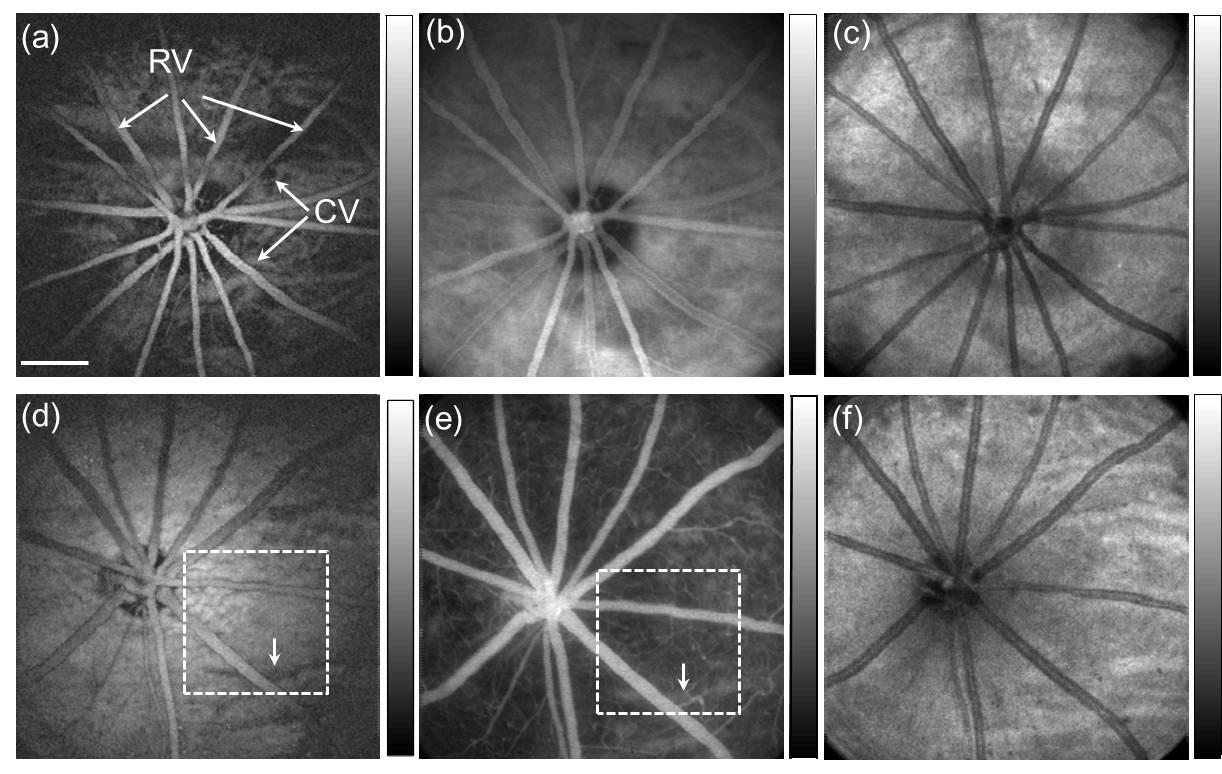
In vivo multimodal retinal imaging of an albino rat (top row) and a pigmented rat (bottom row). Panels (a) and (d) are PAOM fundus images, panels (b) and (e) are FA-SLO images; and panels (c) and (f) are en face SD-OCT images. RV: retinal vessels; CV: choroidal vessels. Bar: 500 µm.
Collaborators:
Prof. Nader Sheibani, Department of Ophthalmology and Vision Science, University of Wisconsin, Madison
Prof. Xiaorong Liu, Department of Biology, University of Virginia
Prof. Joel Schuman, Department of Ophthalmology, Wills Eye Institute
Prof. Tom Kume, Department of Medicine, Northwestern University
Prof. Mark Johnson, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Northwestern University
Prof. Alex Huang, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Diego
Prof. Yang Hu, Department of Ophthalmology, Stanford University
Prof. Jeffrey Goldberg, Department of Ophthalmology, Stanford University
Numerical modeling and image processing
Using Monte Carlo simulation, we try to understand the fundamental limits of existing optical imaging technologies such as funds photograph based retinal oximetry. We are also interested in new image processing methods for quantitative information extraction, better segmentation, and faster reconstruction.
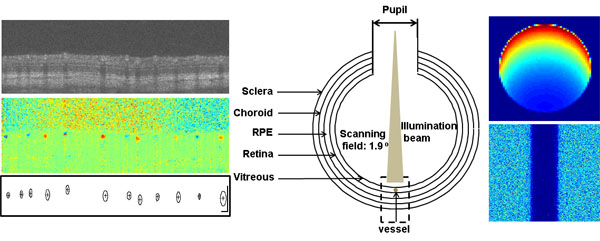
Left: a fast retinal vessel segmentation algorithm that can automatically segment all the major retinal vessels based on OCT phase variation contrast. Right: a Monte Carlo simulation of optical absorption cross section in a vessel and diffusive optical reflection measured from outside the eye.
Research Sponsors
Current
 |
 |
 |
Past
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases |

